CO2 reduction by utilization of waste heat on board of Robin Hood
The most pressing environmental impact from shipping, is the emission of greenhouse gases, especially CO2. In June 2021, IMO adopted key short-term measures aimed at cutting the carbon intensity of all ships by at least 40% by 2030.These measures combine technical and operational approaches to improve the energy efficiency of ships. By 2050, IMO intends to cut the carbon intensity by 70%, as compared to 2008.
The EU has committed to achieve climate neutrality by 2050.
It is evident that implementation of GHG neutral fuel is necessary, from both an environmental, climate and compliance perspective. But it is also evident that it will be years before we can rely purely on sustainable sources of energy. Therefore, we must constantly seek innovations in existing assets and ensure optimal energy efficiency, to keep the negative impact on environment as low as possible and reduce the overall energy cost.
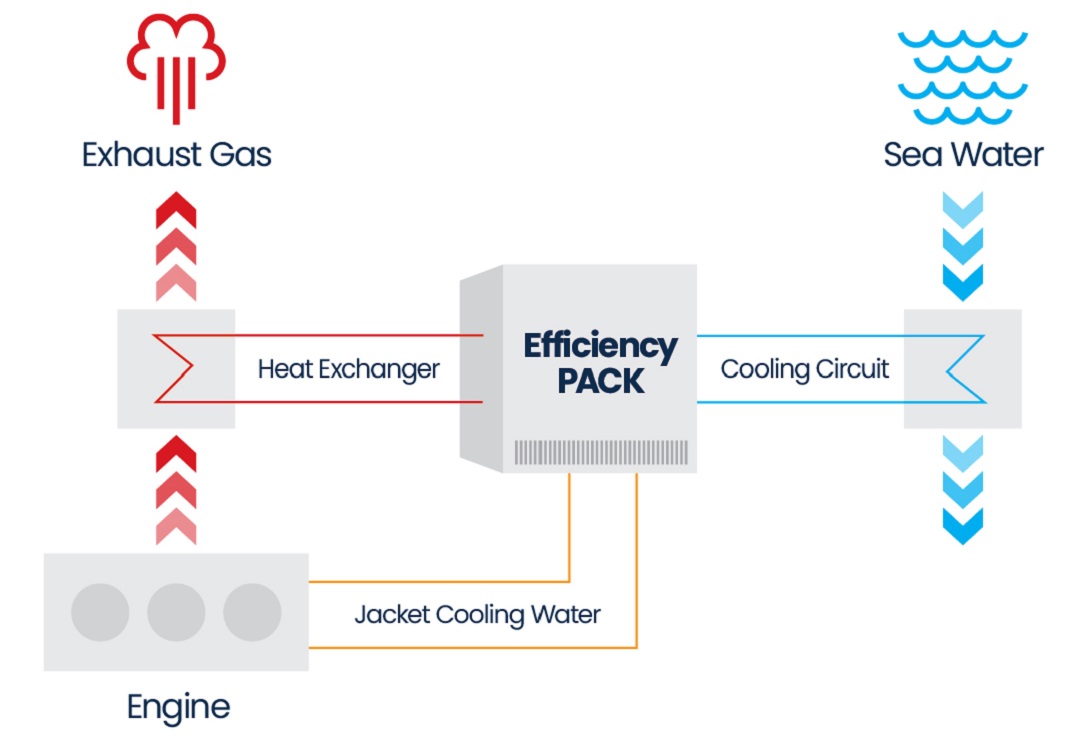
Did you know that the main source of energy loss is in the engine?
For that reason, the improvement of the engine efficiency can lead to significant reduction of the fuel consumption of a vessel. A considerable amount of heat is lost, mainly through the engine's jacket water cooling system and exhaust gases. About one half of the total waste heat is released through the exhaust gases. Additionally, among the different waste heat sources of the ship, the main engine exhaust gases are the most attractive due to their high exergetic content.

Sustainability at TT-Line
Learn more about our sustainable actions and our measures to protect the environment.